The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia recommends the use of vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors for treatment of tardive dyskinesia (TD), irrespective of severity, that has an impact on the patient. Many patients with TD are often on concomitant medications that could interact with VMAT2 inhibitors, and, therefore, it is important to consider pharmacokinetic and metabolic pathways when selecting a new therapy.
TD is a persistent, typically irreversible, hyperkinetic movement disorder resulting from chronic exposure to dopamine receptor blocking agents, including antipsychotic drugs (APDs) and antiemetics, affecting approximately 785,000 patients in the United States.1-4 TD can have a profound impact on many aspects of patients' lives, including their ability to perform daily activities, be productive, and socialize, and can complicate the management of the underlying mental health disorder.5-8
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) guidelines recommend VMAT2 inhibitors, such as AUSTEDO XR, as a first-line treatment option for TD that has an impact on the patient, regardless of severity.9 However, patients diagnosed with TD are often on concomitant medications that may put them at increased risk of drug-drug interactions (DDIs) with VMAT2 inhibitors.10 Therefore, it is crucial to review patients' clinical and medication histories when choosing a therapy for patients with TD.
AUSTEDO XR is one of 2 VMAT2 inhibitors approved in the US for the treatment of adults with TD.11 The following is a summary of the data from the clinical trials with AUSTEDO BID and labelling recommendations for patients who are prescribed AUSTEDO XR while on concomitant medications. Also included below are dosing options for AUSTEDO XR and description of how clinicians can get their patients started on AUSTEDO XR using the 4-week Titration Kit.
The efficacy and safety profile of AUSTEDO was established in 2 pivotal clinical trials, ARM-TD (Aim to Reduce Movements in Tardive Dyskinesia) and AIM-TD (Addressing Involuntary Movements in Tardive Dyskinesia).12,13
ARM-TD (N=113) was a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled flexible-dose clinical trial in which doses were titrated to an individualized dose that reduced abnormal movements and was tolerated.13
AIM-TD (N=222) was a 12-week, fixed-dose trial in which patients were randomized 1:1:1:1 to 12 mg AUSTEDO, 24 mg AUSTEDO, 36 mg AUSTEDO, or placebo per day.12,14
The primary efficacy endpoint in both studies was the change in Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) total score (sum of items 1 through 7) from baseline (defined for each patient as the value from the day 0 visit) to Week 12, as assessed by 2 blinded central video ratings.4,12-14
Patients in the ARM-TD study showed a significant improvement in AIMS total score from baseline (P=0.019) at Week 12 vs placebo (3.0-point reduction vs 1.6-point reduction) (Figure 1).4,13 Results were consistent with those observed in AIM-TD at Week 12.
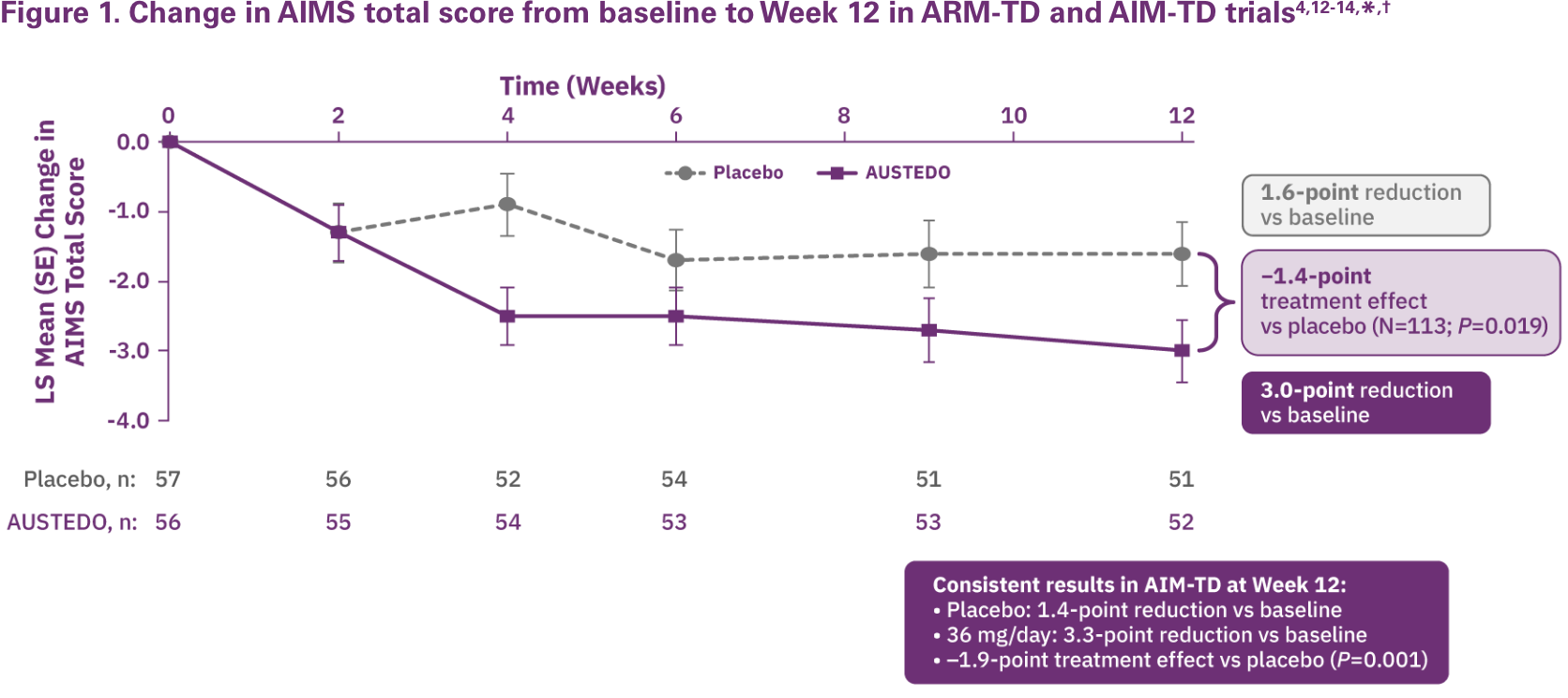
†Patients in the clinical trials received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.12,13
RIM-TD (Reducing Involuntary Movements in Participants With Tardive Dyskinesia) was an open-label, long-term maintenance study in patients who successfully completed ARM-TD or AIM-TD.15 They discontinued AUSTEDO for 1 week and then started at a dose of 12 mg/day, which was titrated for up to 6 weeks.15 The dose was increased in a response-driven manner on a weekly basis by 6 mg/day until the maximum allowable dose was reached, a clinically significant adverse event (AE) occurred, or adequate dyskinesia control was achieved. Patients were followed for approximately 3 years.15
Among the patients evaluated, 337 received treatment at baseline and 163 received treatment through the end of Week 145. During the overall treatment period, patients generally experienced an improvement in AIMS total score.15
Beginning at Week 2 through Week 145, there was a gradual reduction in mean AIMS total score from baseline (Figure 2).15
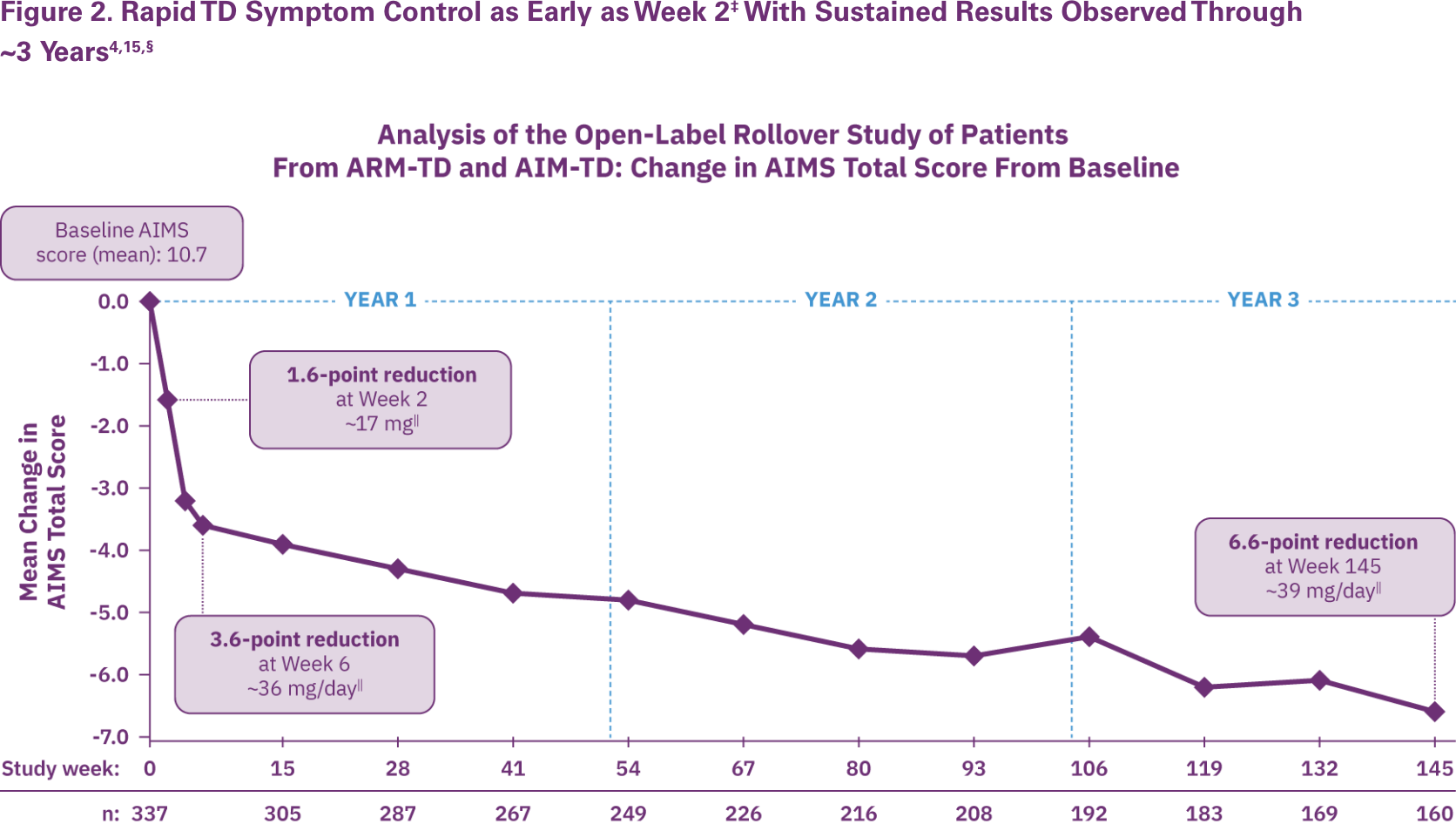
§Patients in the RIM-TD study received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.
||Mean total daily dose.
At Week 145, 67% of patients achieved ≥50% improvement in AIMS total score.15 Preexisting psychiatric scores remained stable throughout the treatment period, and AEs were comparable to those seen in the clinical trials.4,16 The mean overall adherence rate was nearly 90% at 3 years.4
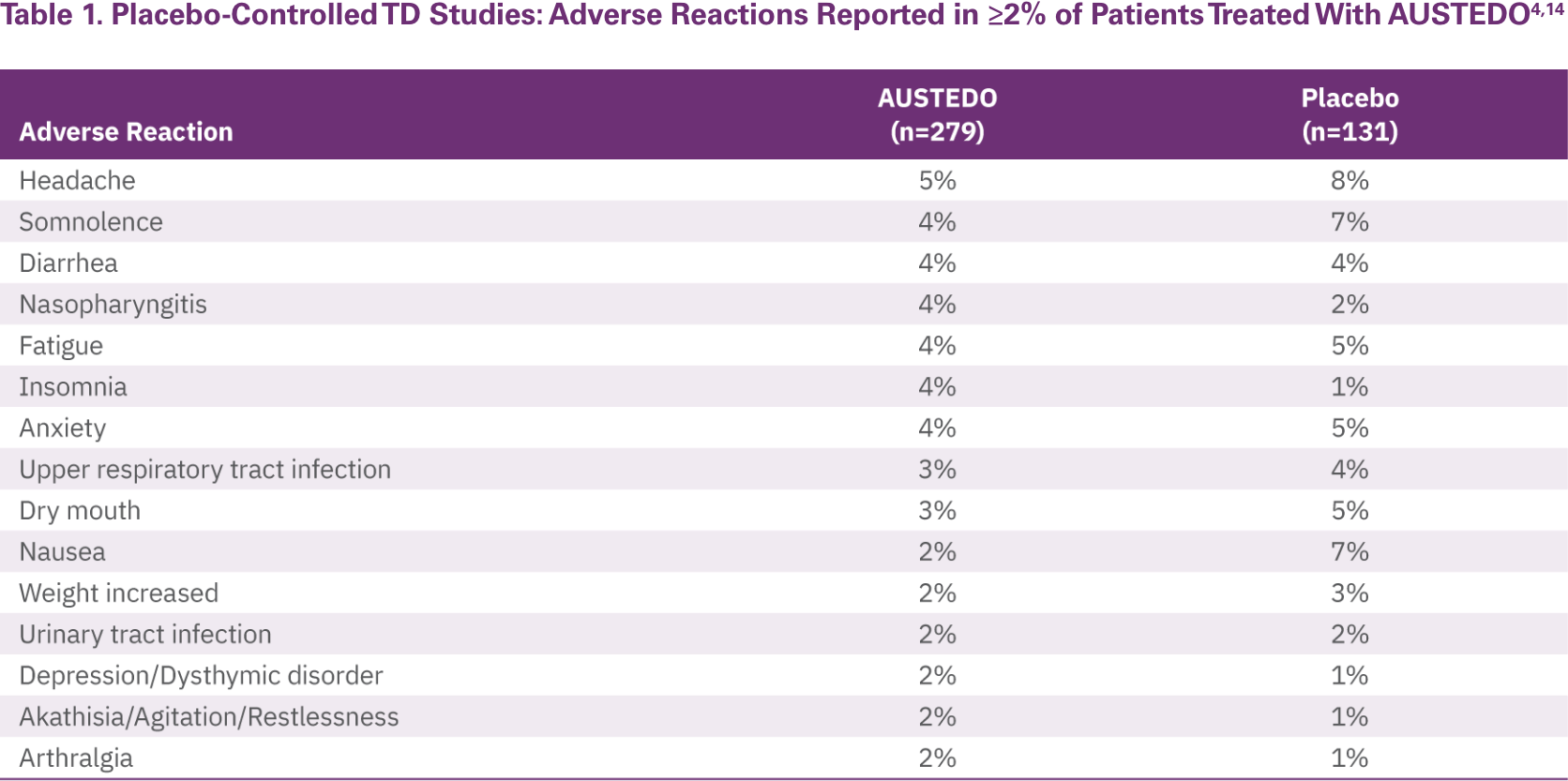
The most commonly reported AEs by patients treated with AUSTEDO (>3% and greater than placebo) in the placebo-controlled studies were nasopharyngitis (4%) and insomnia (4%) (Table 1).14 Discontinuation due to AEs occurred in 4% of patients taking AUSTEDO vs 3% of patients taking placebo.12 Dose reduction due to AEs was required in 4% of patients taking AUSTEDO vs 2% of patients taking placebo.14 Once patients were titrated to their maintenance dose, the following AEs were no longer reported: dry mouth, nausea, and hypertension in AIM-TD and somnolence and dry mouth in ARM-TD.4 Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR are expected to be similar to those with AUSTEDO BID.14
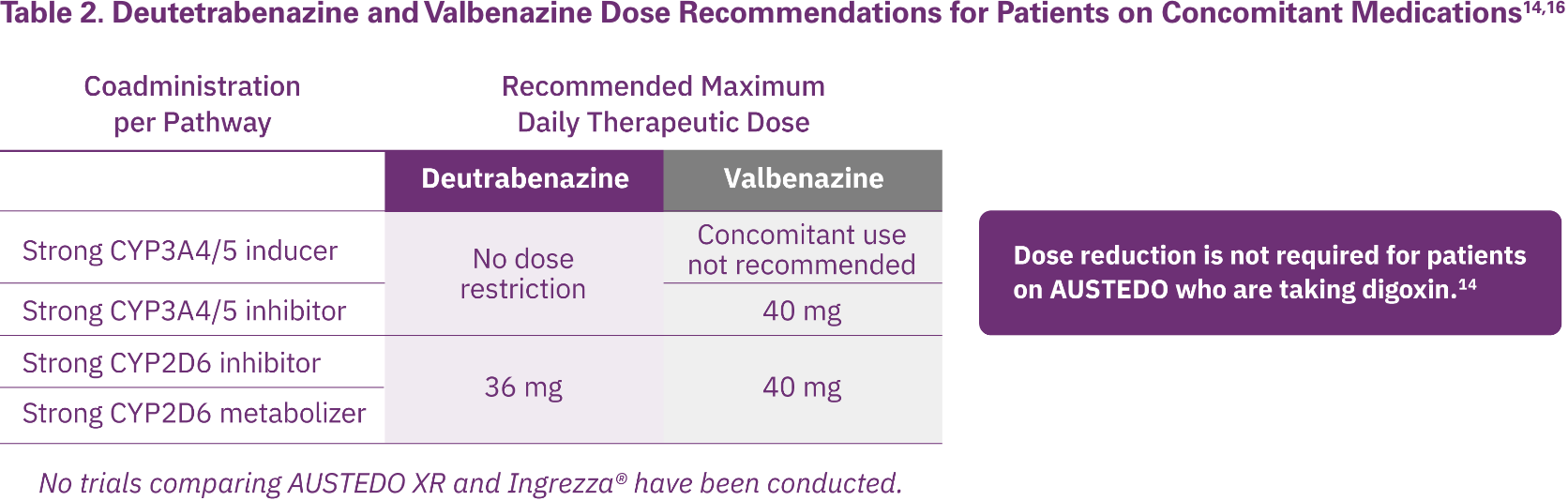
AUSTEDO XR and Ingrezza® are the only FDA-approved medications for TD; they provide different recommendations for dose reductions based on concomitant medications to limit potential DDIs (Table 2).14,16
AUSTEDO XR has no recommendations against concomitant use with CYP3A4/5 inducers or inhibitors and, therefore, should be considered for patients with TD receiving CYP3A4/5 inducers or inhibitors for their comorbidities. AUSTEDO XR is metabolized primarily through CYP2D6, with minor contributions of CYP1A2 and CYP3A4/5, to form several minor metabolites.14
A real-world study evaluating the proportion of patients with newly diagnosed TD potentially at risk of DDIs with VMAT2 inhibitors showed that 20.8% of patients were taking strong CYP2D6 inhibitors, 4.5% were taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, 4.2% were taking strong CYP3A4 inducers, and 0.2% were taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).10
Taking into consideration the listed potential DDIs, it is crucial for clinicians to obtain a list of current medications to avoid unwanted side effects and to review metabolic pathways when choosing a treatment for TD as a means to reduce potential DDIs.14,16
AUSTEDO XR is a once-daily pill available in 6 mg, 12 mg, 18 mg, 24 mg, 30 mg, 36 mg, 42 mg, and 48 mg extended-release tablets.4 The recommended starting dose of AUSTEDO XR for patients with TD is 12 mg/day and may be increased at weekly intervals of 6 mg/day (Figure 3). The range of available dosages offers 5 doses for patients receiving strong CYP2D6 inhibitors.4
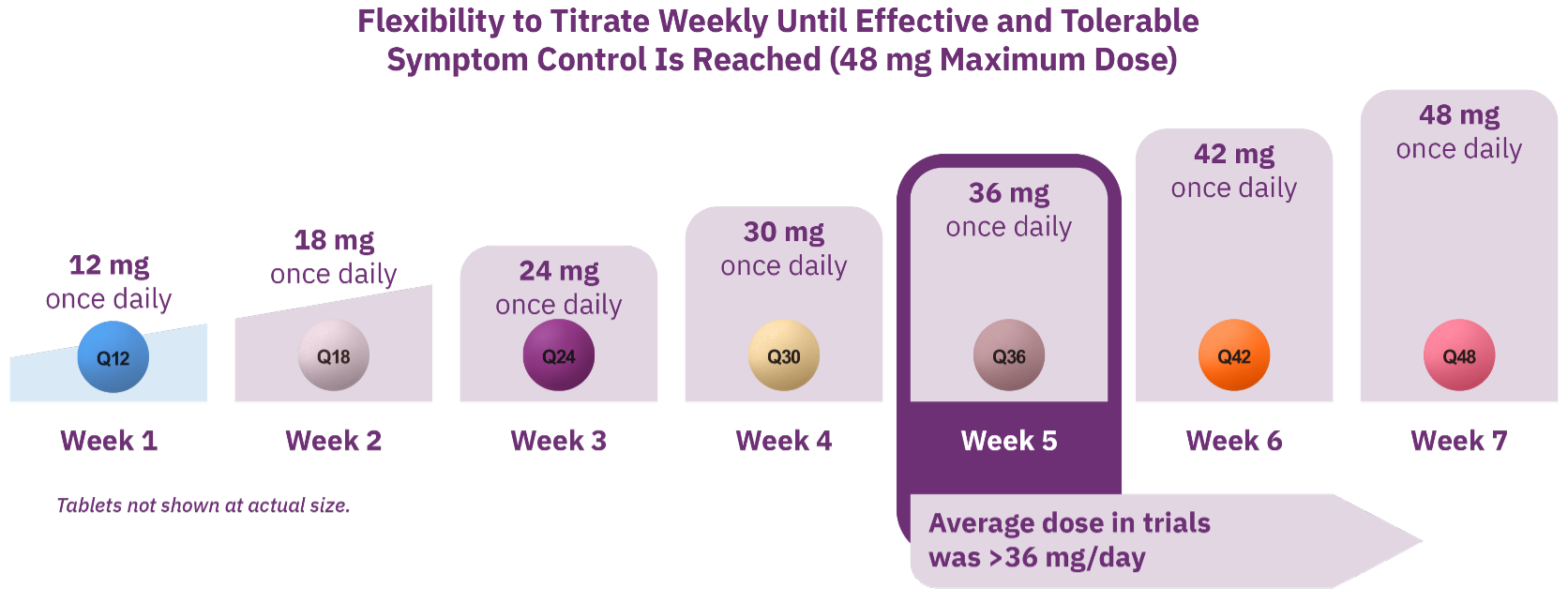
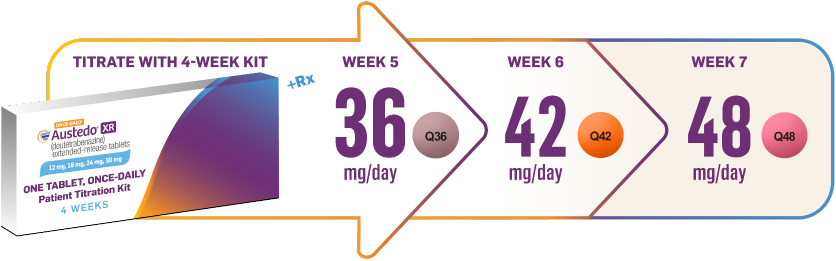
Patients can start on AUSTEDO XR at no cost with the easy-to-use Titration Kit, which brings them to 30 mg/day within the first 4 weeks and is available through sample or prescription (Figure 4).4
The 4-week patient Titration Kits were evaluated in the START Study, a phase 4, non-interventional, 2-cohort (TD and Huntington's disease [HD]), real-world study assessing 4-week Titration Kit utilization and treatment success in 53 patients with TD and 17 patients with HD chorea, both of similar demographics to the AUSTEDO TD pivotal studies.4 In this study, >90% of patients adhered to the Titration Kit, and a majority of patients reached a clinically therapeutic dose range (24-48 mg/day) by Week 4.4
Patients and providers reported overall satisfaction with the Titration Kit and ease of following titration schedule.4
Eligible patients can start at no cost with the 4-week Titration Kit. Exclusions and limitations apply. Refer to AUSTEDOCARDFORM.COM.
#Prescription should not include refills; provide a separate prescription for maintenance dose.
Patients with TD are often on concomitant medications.10 Medications classified as strong CYP2D6 or CYP3A4/5 inhibitors, CYP3A4/5 inducers, or MAOIs have potential to interact with VMAT2 inhibitors.10,11
AUSTEDO XR is the only VMAT2 inhibitor indicated for TD with no recommendations against concomitant use with CYP3A4/5 inducers or inhibitors and therefore, it should be considered for patients with TD receiving CYP3A4/5 inducers or inhibitors for their comorbidities.14
AUSTEDO XR offers 5 dosing options for patients receiving strong CYP2D6 inhibitors who are restricted to 36 mg/day.14
Due to the differences in the metabolism between available VMAT2 inhibitors, clinicians should consider metabolic pathways when choosing a treatment for TD.14,16






